If you’re new to programmatic ads or need a refresher, this guide on programmatic advertising 101 is just for you!
Online advertising can be tricky and time-consuming, often necessitating professional assistance. But programmatic advertising streamlines the process of media buying, making it more efficient.
So whether you’re a marketer, advertiser or simply curious about the digital advertising landscape, this programmatic advertising guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate and leverage the power of programmatic advertising effectively.
Single Grain enables us to increase our impact without increasing our headcount
What Is Programmatic Advertising?
Programmatic advertising is the automated buying and selling of digital ad inventory using technology and data-driven algorithms.
Instead of traditional advertising processes, which might involve RFPs (requests for proposals), negotiations, and manual insertion orders, programmatic buying uses machines and algorithms to purchase display space.
These are the basic features of programmatic advertising:
- Real-Time Bidding (RTB): This is one of the most common types of programmatic advertising, where advertising inventory is bought and sold on a per-impression basis in real-time on the ad exchange. It works much like financial markets, with transactions happening in milliseconds as soon as someone lands on a webpage.
- Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs): Advertisers use DSPs to help them decide which ad impressions to purchase and how much to bid on them, based on a variety of factors such as the sites they appear on, the previous behavior of the user, and the context of the site or page.
- Supply-Side Platforms (SSPs): These are used by online publishers to automate the selling of their ad space. SSPs provide information about the user (without personally identifiable information) to the DSPs to help them decide whether to bid and at what price.
- Data Management Platforms (DMPs): These platforms collect, analyze and manage data from various sources, helping advertisers to target their ads more effectively.
- Ad Exchanges: These are digital marketplaces where publishers and advertisers buy and sell advertising space.
- Programmatic Direct: This form of programmatic advertising is not based on auctions but rather direct buys. In this case, the terms and prices are negotiated beforehand, and the ad impressions are guaranteed (unlike RTB).
By automating the process, businesses can reduce the time and labor associated with the manual handling of ad placements.
The primary advantage of programmatic advertising is efficiency.
Additionally, with the real-time feedback and analytics available, businesses can also more effectively target their desired audiences, adjust their campaigns on the fly, and potentially improve their ROI.
The most striking difference between programmatic and traditional advertising is the use of automation:
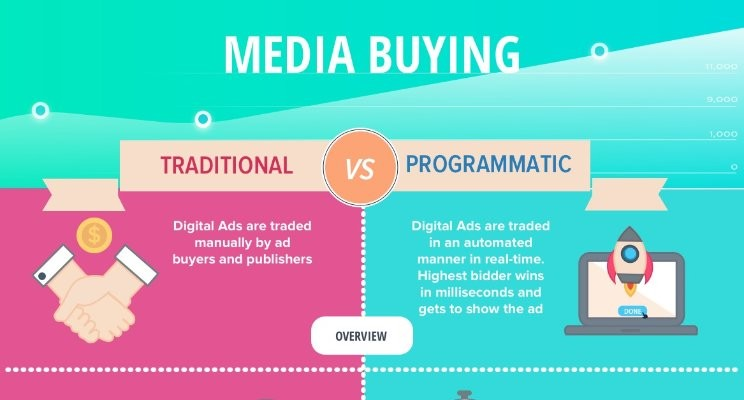
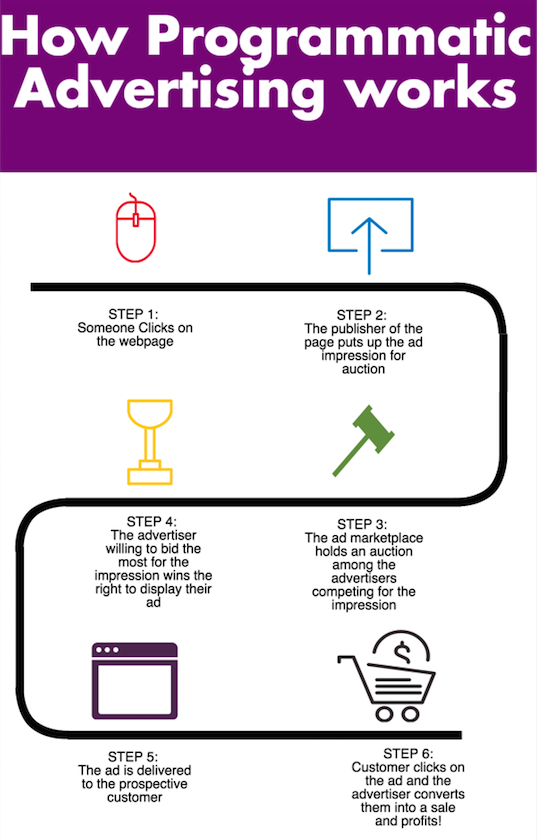
How Programmatic Advertising Works
Here’s a quick look at how programming ads work:
- When a user visits a website or mobile app, an ad impression opportunity is created.
- This information is delivered to an ad exchange, which acts as a marketplace for ad spaces.
- Through demand-side platforms (DSPs), advertisers participate in real-time auctions for ad spaces.
- Advertisers submit their bids during the auction, indicating the maximum amount they are willing to pay for the ad placement.
- The bids are based on the target audience, ad placement relevance, and campaign goals.
- The highest bidder wins the auction, and the ad is served to the user.
Here is an example of a pet shop leveraging programmatic ads:
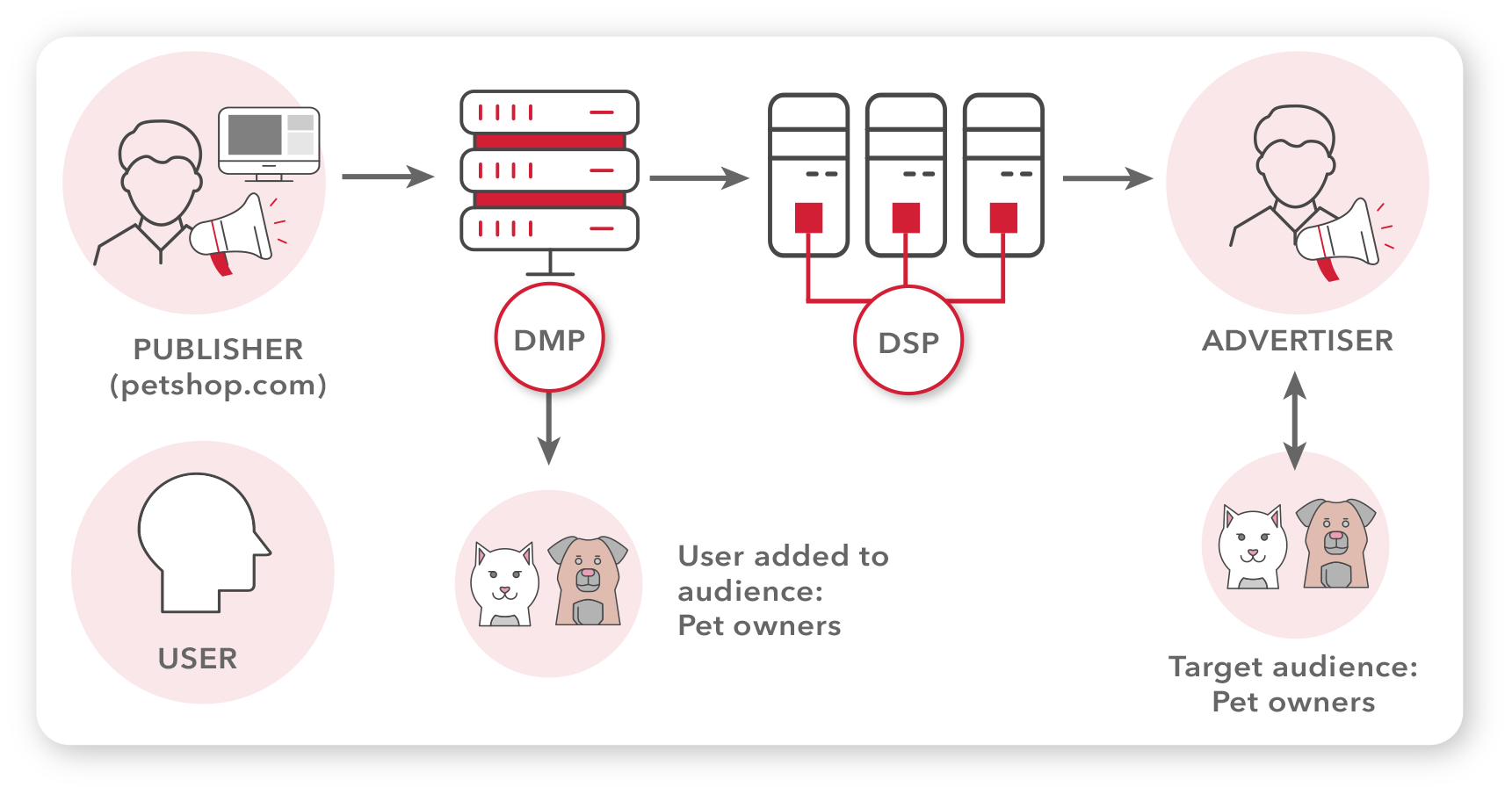
The entire process takes place within milliseconds, from the user visiting the website to displaying the ad. This real-time bidding allows advertisers to precisely target their desired audience and maximize the value of their ad spend.
Why is this important for business owners and entrepreneurs to understand?
A report by Statista states that programmatic advertising spending in the United States will reach an estimated $290 billion U.S. dollars by 2026:
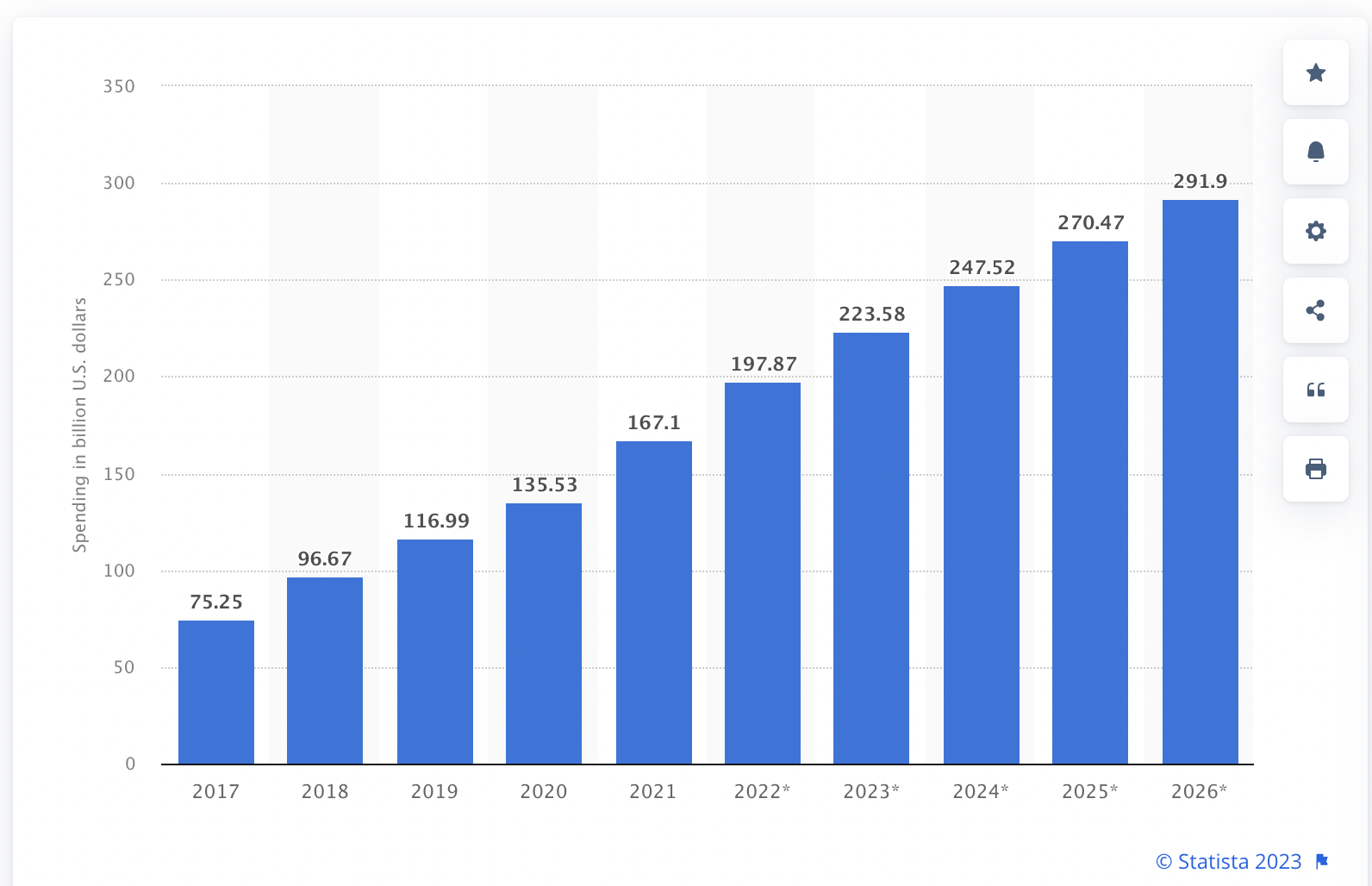
This growth represents an opportunity to promote brand awareness, boost engagement and increase sales.
7 Pillars of Programmatic Advertising
The programmatic ads framework rests on seven key pillars. Knowing these pillars will help you understand how automated digital media campaigns work.
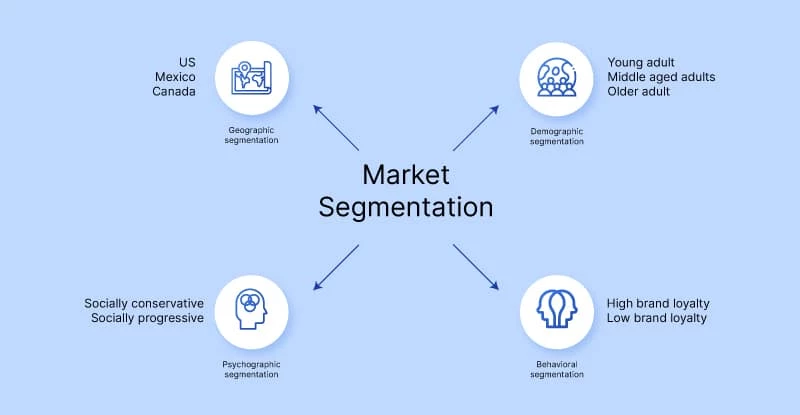
1) Audience
The first pillar of programmatic advertising is the audience. This involves gathering pertinent data to form a detailed audience profile, and then using audience segmentation to ensure that targeted, rather than generic, ad campaigns are delivered:
2) Automation
Automation is a core component of programmatic marketing. It uses technology and algorithms to automate ad buying, optimize campaign performance, and reduce manual marketing efforts.
3) Attribution
Attribution refers to assigning credit to various marketing touch points that contribute to a desired outcome. Programmatic marketing emphasizes the need for accurate attribution models to measure the effectiveness and impact of multiple channels.
4) Integration
Integration involves connecting various systems, data sources and programmatic platforms to ensure a seamless flow of information and campaign management. This pillar integrates different tools and technologies to enhance campaign performance and efficiency.
5) Optimization
Optimization is a continuous process in programmatic marketing. It involves monitoring campaign performance, analyzing data, and making data-driven adjustments to maximize ad effectiveness, reach and ROI.
6) Privacy
Privacy is critical in programmatic marketing, particularly with the increasing focus on data protection and regulations. This pillar emphasizes the importance of maintaining user privacy, complying with data regulations, and transparency in data collection and usage.
7) Transparency
Transparency is essential in programmatic marketing to build trust and credibility. This pillar provides clear and comprehensive reporting, ensures transparent pricing models, and fosters open communication between advertisers, agencies, and technology providers.
8 Types of Programmatic Ads
These are some of the common types, but with the advancement in technology, more types and sub-types of programmatic ads continue to emerge.
The choice of ad format will depend on the specific goals of the advertising campaign, the target audience and the platforms where the audience spends time.
Display Ads
Programmatic Display ads help digital marketers captivate their target audience across various online touch points, including websites, mobile apps, and other digital platforms:

Leveraging visually captivating elements like stunning images or captivating graphics, display ads seamlessly grab users’ attention while concurrently building brand recognition and driving awareness for specific products and services.
Video Ads
Video ads represent a dynamic and captivating format to embed short video clips into online content seamlessly:
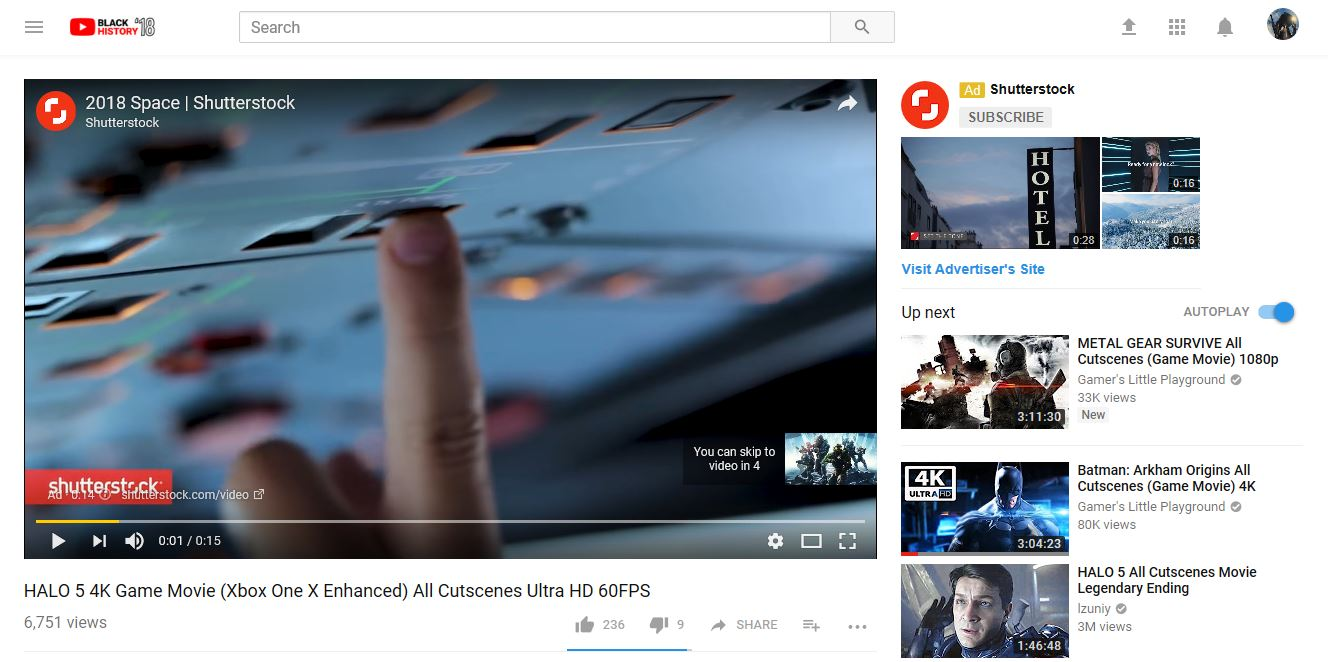
These online ads strategically position themselves before, during, or after the main video, leveraging sight, sound, and motion.
Native Ads
Native ads blend effortlessly with a website or app’s overall look and feel, matching its design and structure:
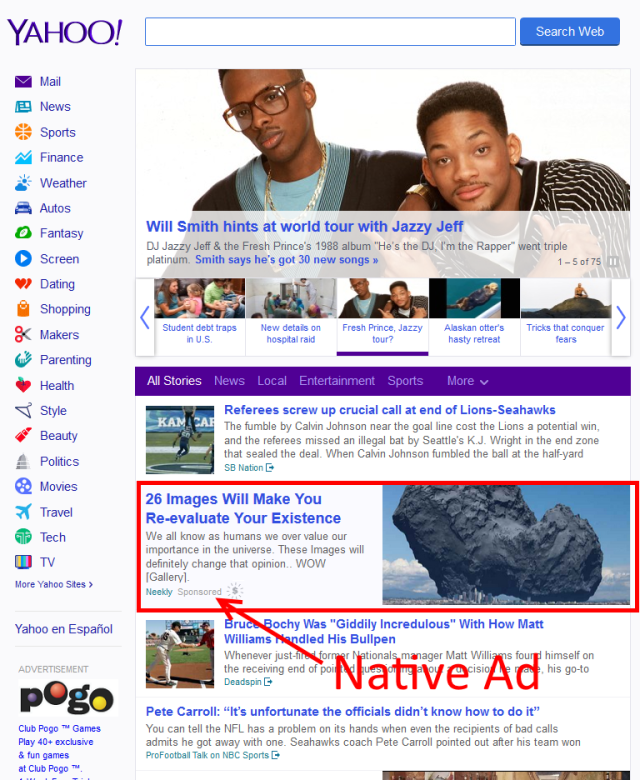
They offer a smooth and uninterrupted advertising experience by appearing as sponsored or recommended content.
Related Content: 11 Native Advertising Trends that You Can’t Ignore
Mobile Ads
Mobile ads are expertly tailored for mobile devices, seamlessly making their presence felt within mobile apps or websites optimized for mobile viewing:
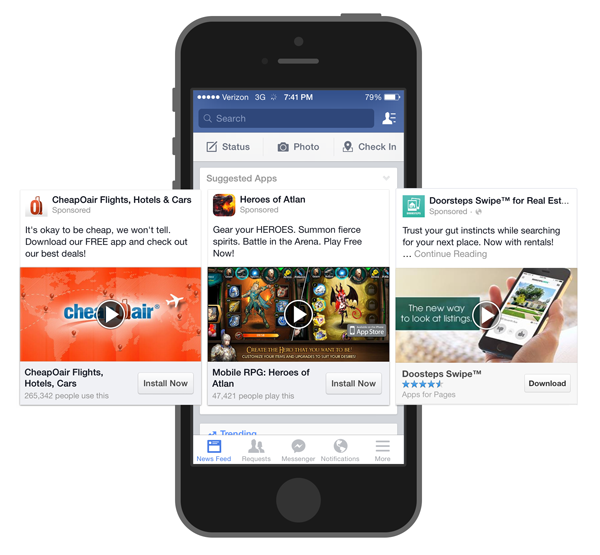
These programmatic technology ads come in various forms, such as banners, interstitials or videos, carefully optimized to suit the smaller screen size and touch interactions of smartphones and tablets.
Audio Ads
Audio ads are smartly crafted advertisements that reach audiences through audio streaming platforms, podcasts, or music apps:
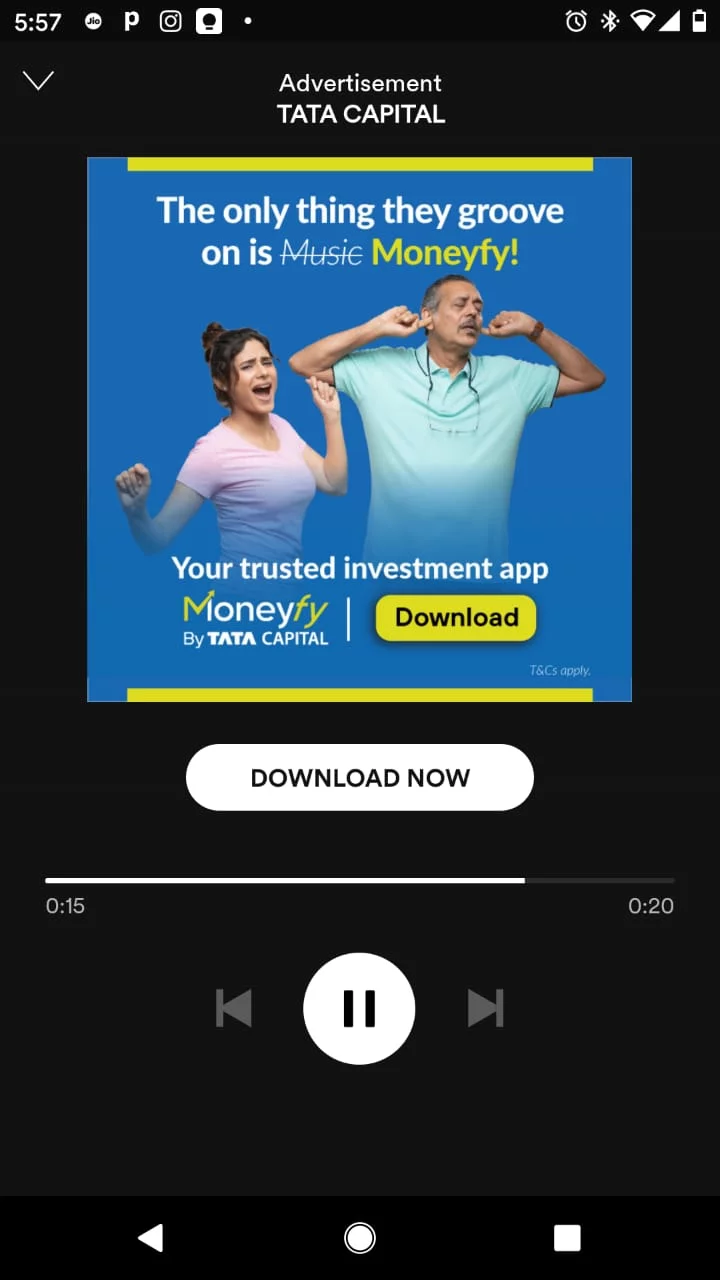
Leveraging the power of spoken words, captivating melodies or catchy jingles, they skillfully convey brand messages and promotional content.
Social Media Ads
Social media ads are served within popular social networking platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, or LinkedIn:

They leverage these platforms’ vast user data and targeting capabilities to reach specific demographics, interests, or behaviors, driving engagement and ad revenue.
Related Content: LinkedIn Ads for Enterprise B2B SaaS: The Only Guide You’ll Need
Connected TV (CTV) Ads
CTV ads are displayed on internet-connected television screens via streaming platforms or smart TVs:
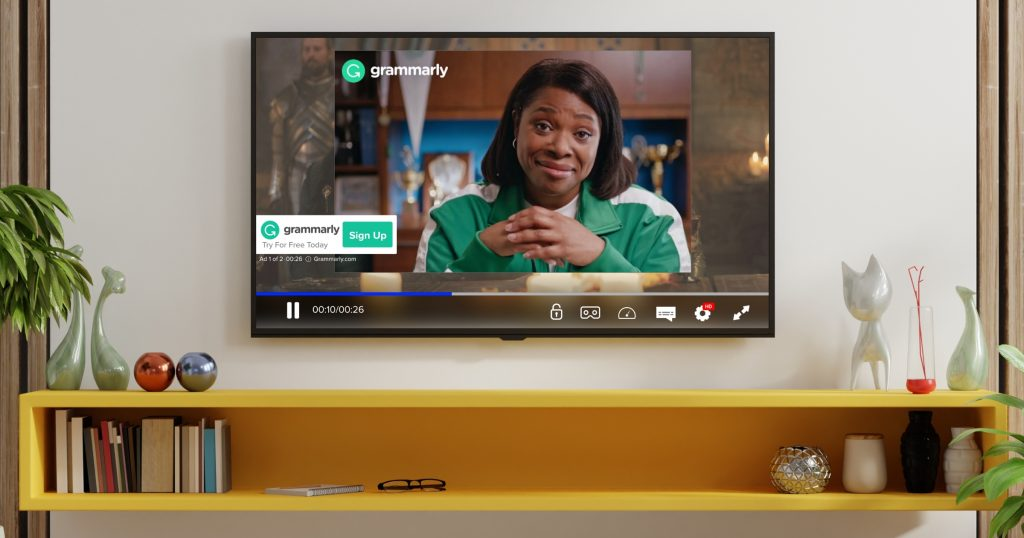
They allow advertisers to reach a larger audience on the big screen and deliver targeted video ads during streaming content, capitalizing on the shift from traditional TV to digital streaming.
Dynamic Display Ads
Dynamic Display ads are personalized and dynamically generated based on user data, preferences, or contextual factors:

This type of advertising delivers highly relevant and customized content, such as product recommendations or pricing, to create a tailored ad experience for each user, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
Benefits of Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is highly popular in the digital marketing landscape. There are several reasons for the importance of programmatic ads in buying and selling digital media.
Here are the top advantages of incorporating these ad types into your advertising strategy:
- They Offer Targeted Reach. Programmatic media buying allows advertisers to target specific audiences with precision. By leveraging data insights and audience segmentation, advertisers can deliver their ads to the right people at the right time, increasing the chances of engagement and conversions.
- They Are Efficient and Cost-Effective. Targeted advertising automates the ad-buying process, eliminating the need for manual negotiations and reduces operational costs. It enables advertisers to optimize their campaigns in real-time, ensuring that their digital ad spend is allocated efficiently and delivering a higher return on investment.
- They Help You Make Better Decisions. AI-powered advertising relies on data-driven decision-making. Using sophisticated algorithms and data analysis, advertisers gain valuable insights into audience behavior, ad performance, and campaign metrics, reducing human error. These insights can be leveraged to refine targeting strategies, improve ad creatives, and drive better results.
- They Provide Greater Transparency and Control. Automatic ad-buying platforms offer transparency in terms of ad placement, ad viewability, and campaign performance metrics. Advertisers can have better control over their campaigns, monitor where their ads appear, and ensure brand safety by excluding undesirable placements.
- They Consider User-Behavior and Personalization. Programmatic advertising relies on user data to deliver personalized and dynamic ads based on user behavior and preferences. Advertisers can customize ad creatives in real-time, tailoring them to specific audience segments and increasing the relevance and impact of their ads.
- They Offer Flexibility and Agility. Automated media buying allows advertisers to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and consumer trends. Campaigns can be modified on the go, enabling advertisers to take advantage of emerging opportunities or adjust strategies based on real-time data.
Disadvantages of Programmatic Advertising
- Ad Fraud and Brand Safety Risks. Although powerful, programmatic advertising faces challenges like ad fraud, where fake or low-quality traffic is generated, resulting in wasted ad spending. Moreover, there is a potential danger of ads appearing on unsuitable or non-brand-friendly websites, which can negatively impact a brand’s reputation.
- Lack of Transparency. Programmatic ad buying operates within a sophisticated network of intermediaries, including ad exchanges, demand-side platforms, and data providers. However, this intricate system often needs more transparency, making it difficult for advertisers to clearly understand how their ad budgets are allocated and where their ads precisely appear.
- Ad Blockers and Ad Fatigue. Ad blockers that block ads from being displayed present a challenge. When people use ad blockers, it restricts the reach and impact of programmatic ads. Moreover, if the ads become repetitive or poorly targeted, they can contribute to a phenomenon known as ad fatigue. This happens when users become immune or frustrated by an overwhelming number of ads, reducing engagement and effectiveness.
- Limited Creative Control. Advertisers often need more support in their creative control and customization level due to reliance on standardized ad formats and templates. Finding a balance between scalability and customization is crucial for ensuring ads stand out and resonate with the target audience.
Related Content: Best Programmatic Advertising Agency: Top 6 Choices for 2023
Programming Advertising Examples
Now that you understand how programmatic ads work and the benefits of using them in your ad campaigns, let’s take a look a few examples.
Personalized Retargeting
Imagine you’re exploring an e-commerce website, checking out a particular category of products, like running shoes. Later, browsing a different website, you see ads showcasing the same running shoes that caught your interest earlier.
This is an excellent example of personalized retargeting made possible through programmatic advertising:
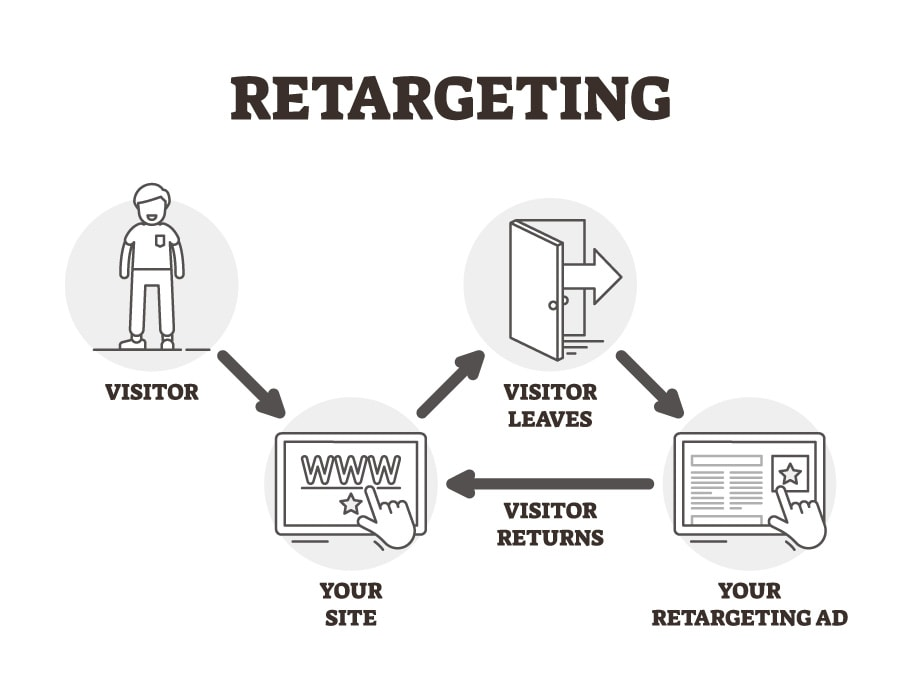
Related Content: Retargeting 101: Why It’s Essential for Any Marketing Funnel
Contextual Targeting
Let’s say you’re reading an article about healthy eating habits on a popular health and wellness website. You see ads for organic food products and fitness equipment when you scroll down the page.
These ads are strategically placed using contextual targeting, which matches the ad content with the surrounding context of the webpage.
Programmatic algorithms analyze the webpage’s content in real-time and deliver ads that align with the user’s current interests and the context of the content they’re consuming.
Here is an example of contextual ad targeting on the Wall Street Journal’s website:

Weather-Based Advertising
Programmatic advertising can leverage weather data to deliver targeted ads based on weather conditions.
Here is an example of a snowstorm ad by snow blower company Ariens that effectively leverages weather-based advertising:

Dynamic Creative Optimization
Automatic digital advertising enables dynamic creative optimization, where ad content is customized and dynamically tailored to individual users. For example, a travel company can display ads featuring different destinations based on users’ geographical locations or past travel preferences.
This personalized approach enhances user engagement and increases conversion rates by delivering highly relevant and compelling ad experiences. Here is an example of a dynamic ad creative where the ad contents are changed in real-time:
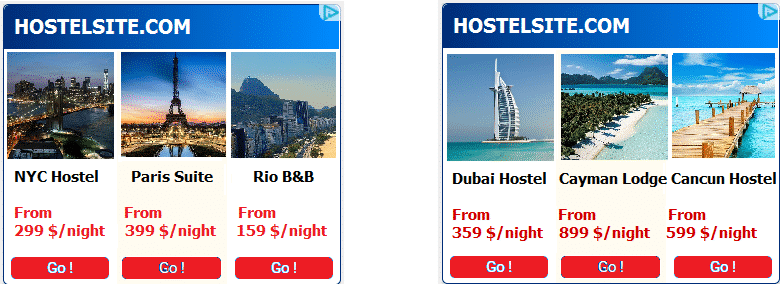
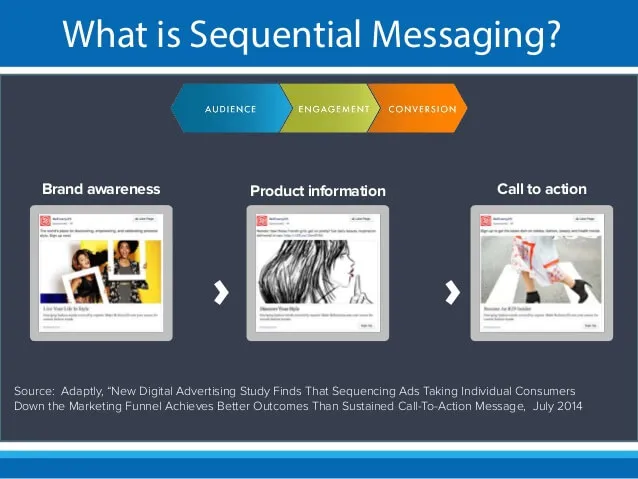
Cross-Device Sequential Messaging
Automated digital ads allow advertisers to deliver sequential messages across multiple devices. For instance, if a user interacts with a brand’s ad on their mobile device, the advertiser can show a follow-up ad with a complimentary offer or additional information on the user’s desktop.
This sequential messaging helps maintain consistency and reinforce brand messaging across different touch points, maximizing the chances of conversion:
You may also like: Content Creation for Programmatic SEO Pages
Future Trends and Innovations in Programmatic Advertising
As I mentioned earlier, with the advancement in technology, we will be seeing more types of programmatic ads in the future. Here are a few future trends.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are set to play a significant role in programmatic advertising. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of cookie data, enabling more accurate audience targeting, ad placement optimization and predictive modeling for campaign performance.
AI-powered algorithms can continuously learn and adapt, driving better campaign outcomes and efficiency.
Advanced Audience Targeting
The future of the automated display advertising process lies in more sophisticated audience targeting capabilities.
Advertisers will employ a data-driven approach to create detailed user profiles, including first-party data, third-party data providers, and connected device data. This will enable precise audience segmentation, allowing advertisers to reach specific target groups with personalized messaging.
Cross-Channel Integration
Programmatic advertising will increasingly focus on cross-channel integration, allowing advertisers to create seamless experiences across multiple platforms and devices.
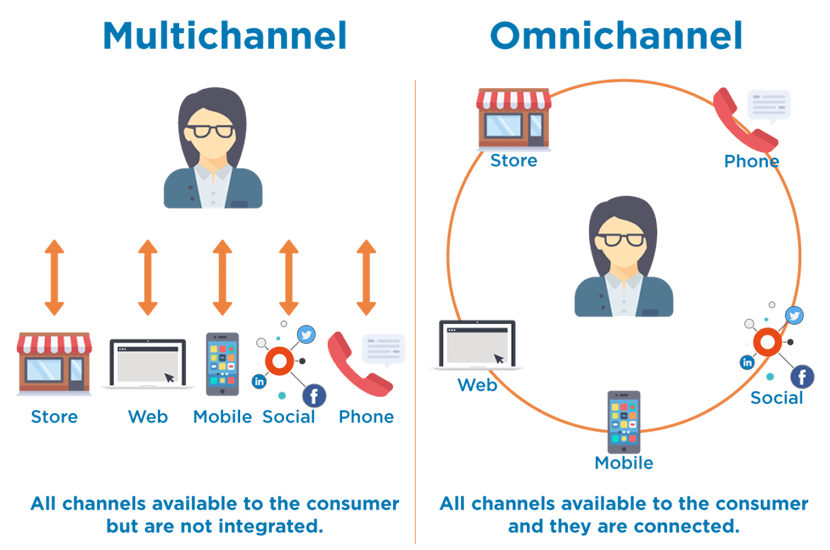
Advertisers will leverage programmatic capabilities to orchestrate and synchronize campaigns across display ads, video, mobile, social media, connected TV, and other emerging channels.
Privacy and Data Protection
Privacy regulations and consumer concerns are shaping the future of programmatic advertising.
Advertisers will adapt to stricter data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Innovations will focus on privacy-preserving techniques like federated learning and contextual targeting to deliver relevant ads while respecting user privacy.
Advanced Ad Formats
Programmatic advertising will continue to evolve in terms of ad formats and interactivity.
Interactive and immersive ad experiences, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) ads, will gain prominence. Advertisers will explore innovative formats to capture users’ attention and create memorable brand interactions.

You may also like: Programmatic SEO for Ecommerce: Scale Your Online Store Fast
Last Word on Programmatic Advertising 101
Programmatic advertising is on the rise, and it’s expected to keep growing and bring more exciting changes to the industry.
The future of programmatic advertising looks promising thanks to advancements in AI, machine learning and cross-channel integration. These technologies will allow advertisers to create ads tailored to each and every person, making the experience more personal and engaging.
By understanding the principles and possibilities of programmatic advertising, you can unlock their potential to drive engagement, increase conversions, and achieve your marketing objectives.
Hopefully you learned all the basics of programmatic advertising! But if you’d just like someone to do all the hard work for you, Single Grain’s programmatic ads experts can help!👇


