Digital rights management (DRM) has been a hot topic in the online world for a while and for a good reason. Despite that, most people probably haven’t even heard of this term. And why would they?
Unless you’re a publisher or content creator, you probably rarely consider how challenging it is to protect content from piracy. However, piracy has been a rampant problem for over a decade now and affects all forms of online media. Here are a few online piracy statistics for 2023 to give you a better perspective:
- Pirated video content gets over 230 billion views a year;
- The TV and film industries suffer s $70bn loss annually due to piracy.
- Around 70,000 jobs are lost due to music piracy in the US alone.
- Over 80% of online piracy is due to illegal video streaming services.
And this data is just what we know for sure. In reality, there are millions of other cases of illegal use, reposting, and content theft on the internet daily. Social media like Twitter and video-sharing websites like YouTube are some of the main breeding grounds for such activity, although they do try to crack down on illegal distribution to an extent.
Since online piracy is such a massive issue, services like DRM are essential to publishers and creators trying to make a living off premium content. This technology has been around for a long time. During that time, it has been perfected to help businesses and creators protect their digital IPs. But what is DRM exactly, how does it work, and does your business really need it? Let’s find out!
- A Brief History of Digital Rights Management
- What Is Digital Rights Management (DRM) in Online Publishing
- What Is DRM-Protected Content in Online Publishing?
- How Does DRM Protection Work Behind the Scenes
- What Are Some Examples of DRM in Practice?
- Why (and When) Do Publishers Need DRM Protection?
- How TargetVideo Can Help Publishers Protect Their Videos With DRM
- FAQ
A Brief History of Digital Rights Management

Do you remember these little buggers? We most certainly do!
When the first MP3 players like this one appeared in the 90s, they threw the music industry into an uproar. Record labels worldwide feared the rapid digitalization of the industry. They predicted that this technology would give unprecedented rise to piracy.
They were right.
Although piracy existed before the popularization of the MP3 container, it was much harder (and more expensive) to pull off. This was because it mainly dealt with physical copies.
However, with the new MP3 format, copying and transferring files illegally became much easier. Thanks to portable MP3 players, anyone could exchange and transfer music in a few clicks. There was seemingly no way to prevent that… or was there?
When Apple released its iPod in 2001, it brought with it one of the earliest forms of anti-piracy measures. Unlike regular MP3 players, the iPod prevented users from freely moving MP3 files off of the device. Instead, the music files would be stored on Apple’s online servers, safeguarding the content behind a unique encrypted ID. That meant people couldn’t copy the same digital music files freely between devices anymore.
Fast forward to today, and dozens of industries worldwide use a similar system now to help publishers and content creators protect their digital IPs — DRM.
What Is Digital Rights Management (DRM) in Online Publishing
Digital rights management (DRM) is a technology that protects digital copyright by managing and limiting access to copyrighted digital media. DRM software also includes various measures against unauthorized copying, distribution, and modification of said copyrighted materials.
DRM technology gives publishers and content creators full control over who can access their content and what they can do with it. It protects their IPs and prevents their work from theft and illegal distribution online. All of this makes DRM the cornerstone of any online business relying on the selling and distribution of exclusive and premium content.
Although DRM doesn’t combat and pursue those who engage in piracy, it prevents your content from falling victim to it in the first place.
What Is DRM-Protected Content in Online Publishing?
DRM-protected content is any content that has various restrictions on how people can access or use it. Almost any type of digital content can be protected in this way. The most common types of DRM-protected content include:
- E-books
- Videos
- Music
- PDF Files
- Images
- And more…
Content protected by DRM technology usually has various safeguards that limit how users can interact, edit, or distribute it. In other words, DRM works by protecting publishers’ content in the following ways:
- Prevent users from editing or saving content;
- Limit or prohibit sharing or forwarding of a specific product or content;
- Restrict or limit users from printing specific content;
- Prevent users from screenshotting a product or content;
- Set expiration dates on online documents, pieces of media, or content;
- Lock specific content pieces for certain IP addresses, GEO locations, or devices;
- Watermark visual or video content or documents to establish ownership.
As you can see, publishers and content creators have plenty of freedom and customization options for their DRM-protected content. That is the primary reason this technology is the go-to choice for piracy prevention for millions of businesses worldwide.
How Does DRM Protection Work Behind the Scenes
Digital rights management works by encrypting digital files and locking them behind a unique ID. This ensures that only specific devices or users that meet certain criteria can access them. In other words, it prevents third parties from accessing these media files without authorization.
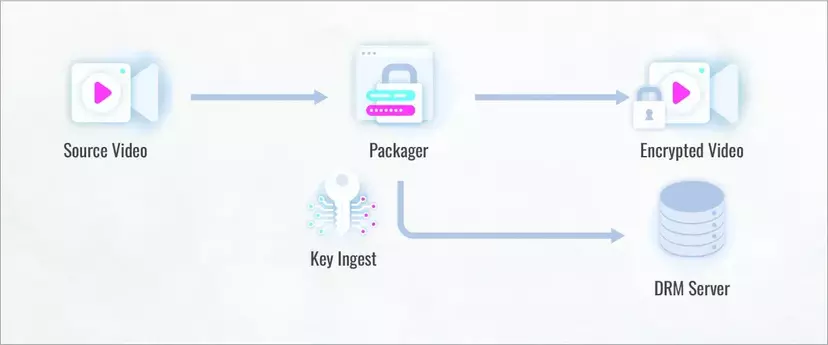
Here’s a step-by-step illustration of how DRM works on an example of online video:
- Encryption Key Generation: When the IP owner uploads a video file to their platform, the file gets a unique encryption key from the DRM provider. This key is uploaded to the DRM platform.
- Sending the Key: The platform encrypts the video file and sends the key and the necessary metadata to a license server for distribution.
- File Packaging: When the publisher uploads the video to their platform, the encrypted version of the file is packaged and sent instead.
- Access Verification Request: When a user tries to play content, the HTML5 player sends a request to the owner’s proxy to verify whether they have the right to access the piece of content.
- Sending the Decryption Key: If the copyright holder’s website or service validates the user’s access rights, it communicates with the DRM platform and sends the license/decryption key to enable playback. The same process happens if the user tries to download the content.
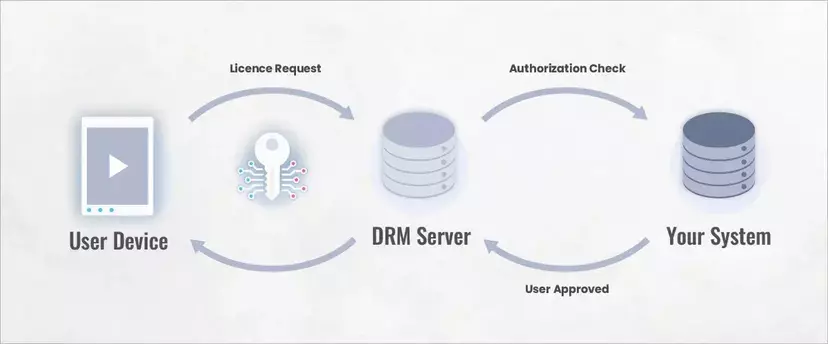
As you can see, the DRM system functions as a sort of lock that only a specific key (decryption key) can open. And since the license server is in charge of distributing these keys, only users with valid licenses (those who purchased the product) will be able to access your content.
What Are Some Examples of DRM in Practice?
Now that you’re familiar with how DRM works, here are a few real-life examples of it:
- Apple iTunes — iTunes was one of the first services to implement DRM. It relies on it to control which users can access and download audio files. That prevents users from illegally distributing music without purchasing the rights to it.
- Music Streaming Services (e.g., Spotify) — Music streaming platforms like Spotify or Deezer use DRM technology to track the time users spend streaming different artists’ music and calculate the royalties each party gets for their work.
- Private Documents (e.g., Watermarking) — Many businesses worldwide use DRM to restrict access to their important documents. DRM lets them track the original versions of these files, any edits, and copies, and designate what people can alter in them. That is most useful when making long-distance contracts, as it improves these documents’ security and legitimacy.
- Computer Software (e.g., Microsoft Windows) — Most downloadable computer software nowadays comes with a unique license number and key that allow IP owners to track and control who has access to their content. One of the most famous examples is the Microsoft Office Suite.
- OTT Streaming Services (e.g., Netflix) — Dozens of OTT services like Netflix, Hulu, or Disney+ rely on DRM technology to ensure only users who’ve paid a subscription fee or bought a piece of content can stream it.
Despite its widespread use and versatility, DRM is not a be-all-end-all solution. In fact, not everyone needs to protect their digital IPs.
Some industries rely (and depend) on users sharing their content to survive and won’t have much use of DRM. So it’s only natural for publishers to ask the million-dollar question — how do I know if I need DRM?

Why (and When) Do Publishers Need DRM Protection?
Publishers need DRM technology for an array of reasons, such as restricting access to confidential information or protecting themselves from revenue loss. But first, let’s take a look at some scenarios where you might not need DRM.
When Don’t You Need Digital Rights Management
If you are a publisher working in the online media space and rely on AVOD to monetize your content, you might not need absolutely everything that DRM has to offer. The reason is simple — publishers who rely on ad-based monetization don’t need to restrict how and which users see their content. Quite the contrary — they want as many people to interact with it as possible.
The more people watch and share your videos, the more video ad revenue you’ll earn. So there’s no tangible reason to restrict content sharing or limit user access.
However, even as an AVOD publisher, you still might need certain aspects of DRM. Namely, by allowing users to download your content freely, you are losing out on potential ad revenue. So protecting your content from unauthorized downloads is definitely something to consider.
Why Do You Need Digital Rights Management (DRM)
There are many reasons why publishers should consider getting DRM protection:
- Data Protection. With DRM, publishers ensure that only those persons authorized to view a certain type of content can access it. This is especially important for confidential information where leaks could significantly impact the company’s operations.
- Revenue Protection. If a publisher’s revenue depends on restricting access to content, such as in SVOD and TVOD streaming services, DRM can be the difference between maximizing income and losing paying customers.
- Distribution Control. Aside from restricting direct access to content, DRM can ensure that those who have the authorization to view your videos cannot distribute them to those who don’t.
- Brand Image Protection. Allowing users to freely access, edit, and distribute your content can result in the deterioration of the image your brand maintains in the public eye, be it due to the potential spreading of misinformation or poor content quality.
- Regulatory Compliance. Ensuring compliance with industry regulations is crucial, especially for publishers that distribute third-party content. No production company will want to work with a publisher who can’t ensure the utmost safety and protection of their content.
How TargetVideo Can Help Publishers Protect Their Videos With DRM
If you’re a publisher looking for a reliable way to monetize videos or live streams while ensuring your content is safe from theft, TargetVideo can help you.
TargetVideo’s HTML5 player is fully compatible with Google Widevine, Microsoft PlayReady, and iOS Fairplay DRMs. That means publishers using one of these DRM solutions can easily integrate them with our player to protect their content.
If you aren’t using any of these providers but still want to protect your content from theft, you can still do that with our third-party partner, EZDRM.
So whether you’re a publisher looking for a safe video monetization solution or wish to launch a VOD service, you can easily do so with TargetVideo.
Want to learn more about our DRM solution and how to set it up? Get in touch with our sales team.

FAQ
1. What is DRM software?
DRM software is a program or solution that helps companies and brands protect their digital IPs and exercise greater control over how users can interact and what they can do with their content.
2. What is a DRM license?
A DRM license is a technological framework of encryptions that DRM software uses to protect copyrighted content online and prevent its illegal distribution.
3. What is DRM encryption?
DRM encryption is the process digital rights management software uses to encrypt copyrighted media files to prevent third parties and unauthorized users from accessing, editing, or sharing them illegally.
4. How does DRM encryption work?
DRM encryption works on the lock-and-key principle. Each encrypted file can be accessed only with a specific decryption key. The DRM software handles the distribution of these keys. That way, only users who have met specific criteria (e.g., paid for the content) can access these files.
5. What is protected by DRM?
You can use DRM to protect almost any kind of online media or content. Some of the content that can be protected includes but is not limited to:
- E-books
- Music
- Videos
- Images
- PDF files
- And more…
6. What is a DRM-protected file?
A DRM-protected file is a media file encrypted by DRM software to protect it from unauthorized access, editing, and copying.
